| Mark 43 torpedo | |
|---|---|
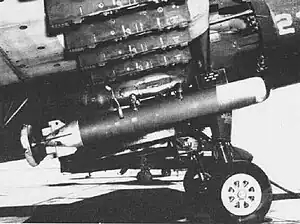 Mark 43 torpedo mounted on an AD Skyraider | |
| Type | Antisubmarine torpedo[1] |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1951–57[1] |
| Used by | United States Navy Royal Navy |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Brush Development Company[1] Naval Ordnance Test Station Pasadena |
| Designed | 1950[1] |
| Manufacturer | Brush Electronics Company[1] |
| Produced | 1951–59 |
| No. built | 5000[1] |
| Variants | Mark 43 Mod 1[1] Mark 43 Mod 3[1] |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 265 pounds (Mod 3)[1] |
| Length | 91.5 inches[1] |
| Diameter | 10 inches[1] |
| Effective firing range | 4500 yards (Mod 3)[1] (6-minute search duration) |
| Warhead | Mk 100, HBX (Mod 3)[1] |
| Warhead weight | 54 pounds (Mod 3)[1] |
Detonation mechanism | Mk 19 Mod 13 contact exploder[1] |
| Engine | Electric[1] |
| Maximum speed | 21 knots (Mod 3)[1] |
Guidance system | Helix search[1] |
Launch platform | Helicopters, fixed-wing aircraft, and surface ships[1] |
The 10" Mark 43 torpedo was the first and smallest of the United States Navy light-weight anti-submarine torpedoes. This electrically propelled 10-inch (25-cm) torpedo was 92 inches (2.3 m) long and weighed 265 pounds (120 kg).[2] Described as "a submersible guided missile",[3] the torpedo was designed for air or surface launch. The Mod 0 configuration was designed for launch from helicopters or fixed-wing aircraft, and the Mod 1 configuration was for helicopters only. Both were electrically driven and deep-diving, but had relatively short range. They were classified as obsolete in the 1960s.[2]
The Royal Navy purchased fifty examples of the Mark 43 in favour of an improved version of their 18 inch Mark 30 "Dealer B"
See also
References
Citations
Bibliography
- Kurak, Steve (September 1966). "The U. S. Navy's Torpedo Inventory". United States Naval Institute Proceedings.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.